Outline
- Introduction
- Importance of a skilled team during childbirth
- Overview of the childbirth process
- Role of healthcare professionals
- Obstetrician-Gynecologist (OB-GYN)
- Role and responsibilities
- Education and training
- Guidelines for newborn and maternal care
- Midwife
- Types of midwives (CNMs, CPMs)
- Role in childbirth and postpartum care
- Benefits of midwifery care
- Labor and Delivery Nurse
- Duties during labor and delivery
- Support for the mother and family
- Best practices for newborn care
- Anesthesiologist
- Role in pain management during childbirth
- Types of anesthesia used
- Safety measures and protocols
- Neonatologist
- Care for newborns with complications
- Collaboration with other healthcare providers
- Steps for newborn health assessment
- Pediatrician
- Initial care for newborns
- Monitoring infant health post-delivery
- Guidelines for newborn health
- Doula
- Support for emotional and physical needs
- Differences between a doula and a midwife
- Importance of continuous support during childbirth
- Lactation Consultant
- Assistance with breastfeeding
- Education and support for new mothers
- Tips for successful breastfeeding
- Perinatal Social Worker
- Emotional and social support for families
- Resources and referrals for additional help
- Addressing mental health and postpartum depression
- Sonographer
- Role in prenatal care and monitoring
- Use of ultrasound technology
- Importance of accurate fetal assessment
- Conclusion
- Importance of a collaborative team for safe delivery
- Final thoughts on supporting new parents
- Guidelines for healthy newborn care and maternal recovery
10 Healthcare Professionals That Help Deliver a Baby
Introduction
The birth of a child is a momentous occasion, filled with excitement and anticipation. However, it is also a complex medical event that requires the expertise and collaboration of a skilled team of healthcare professionals. From the early stages of pregnancy to the delivery and postnatal care, these professionals play a crucial role in ensuring the health and well-being of both the mother and the newborn.
if you love music then you should visit
This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the ten key healthcare professionals involved in the childbirth process. Each section will explore the specific roles, responsibilities, and contributions of these professionals, highlighting best practices for ensuring a healthy delivery and postnatal period. Additionally, the article will offer guidance for both doctors and mothers on essential steps to follow for the good health of the baby and mother, emphasizing the importance of a comprehensive and informed approach to childbirth.

1. Obstetrician-Gynecologist (OB-GYN)
Role and Responsibilities:
An Obstetrician-Gynecologist, commonly known as an OB-GYN, is a physician specializing in the medical and surgical care of the female reproductive system. They are trained to manage all aspects of pregnancy, labor, and delivery, making them integral to the childbirth process. OB-GYNs are responsible for:
- Prenatal Care: Conducting regular check-ups to monitor the health of the mother and fetus, performing ultrasounds, and ordering necessary tests to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
- Labor and Delivery: Managing the labor process, performing vaginal deliveries, and conducting cesarean sections (C-sections) if needed.
- Postpartum Care: Providing care and support to the mother after delivery, addressing any complications, and ensuring proper recovery.
Education and Training:
To become an OB-GYN, one must complete a bachelor’s degree, followed by medical school, earning a Doctor of Medicine (MD) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degree. After medical school, they undergo a four-year residency program in obstetrics and gynecology, where they gain hands-on experience in managing pregnancy and childbirth. Some OB-GYNs may choose to pursue further specialization through fellowship programs.
Guidelines for Newborn and Maternal Care:
OB-GYNs play a critical role in ensuring the health of both the mother and newborn. They should adhere to the following guidelines:
- Promote Healthy Practices: Educate expectant mothers on proper nutrition, exercise, and prenatal care to support a healthy pregnancy.
- Monitor High-Risk Pregnancies: Identify and manage high-risk pregnancies with specialized care and interventions to prevent complications.
- Ensure Safe Delivery: Follow evidence-based practices and protocols to ensure a safe and successful delivery, whether vaginal or cesarean.
- Support Postpartum Recovery: Provide guidance on postpartum care, including wound healing, pain management, and emotional support for the mother.
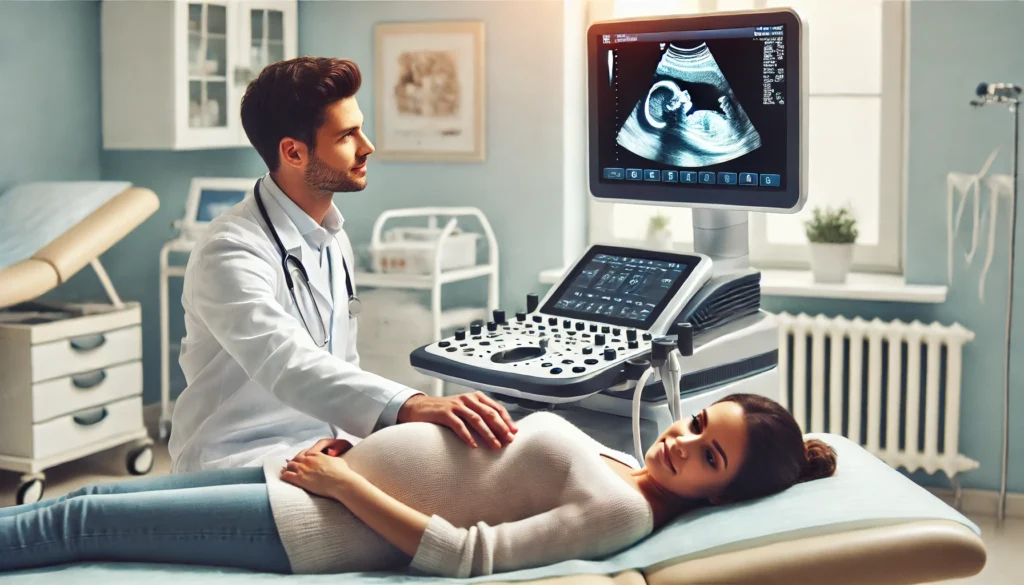
2. Midwife
Midwives are healthcare professionals who specialize in supporting women during pregnancy, labor, and the postpartum period. They offer a personalized and holistic approach to childbirth, focusing on natural and low-intervention methods.
Types of Midwives:
- Certified Nurse-Midwives (CNMs): Registered nurses with advanced training in midwifery, CNMs are licensed to provide comprehensive care in various settings, including hospitals, birthing centers, and homes.
- Certified Professional Midwives (CPMs): Specializing in out-of-hospital births, CPMs provide care in homes and birthing centers, focusing on personalized and natural childbirth experiences.
Role in Childbirth and Postpartum Care:
Midwives are responsible for:
- Prenatal Support: Conducting regular prenatal visits, providing education on childbirth, nutrition, and lifestyle choices, and offering emotional support to expectant mothers.
- Labor and Delivery: Assisting with natural childbirth, utilizing techniques for pain management and comfort, and supporting the mother throughout the labor process.
- Postpartum Care: Offering continued support and guidance to the mother and newborn after delivery, assisting with breastfeeding, and monitoring the health and well-being of both.
Benefits of Midwifery Care:
- Personalized Attention: Midwives provide individualized care, building strong relationships with their clients and addressing their unique needs and preferences.
- Empowerment and Education: Midwives empower women to take an active role in their childbirth experience, providing education and resources to support informed decision-making.
- Holistic Approach: Midwifery care emphasizes a holistic approach, focusing on the physical, emotional, and social aspects of childbirth and postpartum recovery.

3. Labor and Delivery Nurse
Labor and delivery nurses are registered nurses who specialize in caring for women during labor and childbirth. They play a vital role in ensuring a safe and positive birthing experience, providing support and care to both the mother and the newborn.
Duties During Labor and Delivery:
Labor and delivery nurses are responsible for:
- Monitoring: Tracking the mother’s vital signs and the baby’s heart rate to ensure both are stable and healthy throughout labor.
- Support: Providing emotional and physical support to the mother, assisting with pain management techniques, and encouraging positive coping strategies.
- Collaboration: Working closely with OB-GYNs, midwives, and other healthcare professionals to ensure seamless communication and coordination of care.
Support for the Mother and Family:
Labor and delivery nurses are often the primary source of support for the family during childbirth, offering reassurance, guidance, and education throughout the process. They help create a positive and empowering environment, addressing the family’s concerns and providing resources for postnatal care.
Best Practices for Newborn Care:
- Immediate Assessment: Perform a thorough assessment of the newborn immediately after birth, checking for signs of distress and ensuring proper adaptation to the external environment.
- Promote Skin-to-Skin Contact: Encourage skin-to-skin contact between the mother and newborn, fostering bonding and supporting breastfeeding initiation.
- Monitor Vital Signs: Continuously monitor the newborn’s vital signs, including temperature, heart rate, and respiratory rate, to ensure stability and detect any potential issues early.

4. Anesthesiologist
Anesthesiologists play a vital role in childbirth by ensuring the mother’s comfort and safety during labor and delivery. Their expertise in pain management allows for a smoother and less stressful birthing process.
Safety Measures and Protocols:
Anesthesiologists adhere to strict safety protocols to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the newborn:
- Pre-Procedure Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of the mother’s medical history, allergies, and current medications to determine the most appropriate anesthesia plan.
- Continuous Monitoring: Monitor the mother’s vital signs and level of consciousness during the administration of anesthesia, making necessary adjustments to maintain stability.
- Emergency Preparedness: Be prepared to address any adverse reactions or complications related to anesthesia, ensuring prompt intervention and support.
Anesthesiologists also play a crucial role in educating mothers about the available pain relief options, helping them make informed decisions about their childbirth experience.
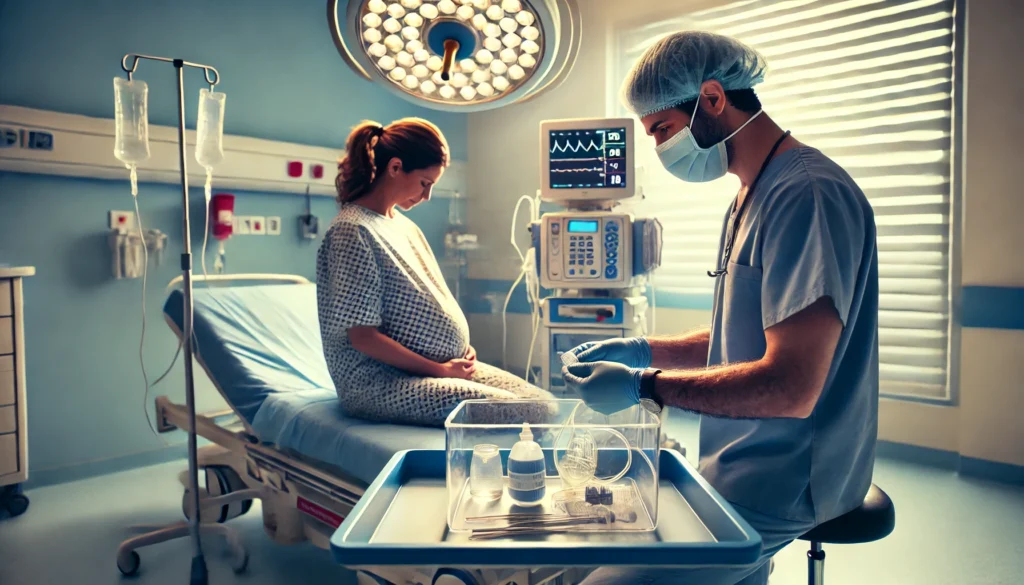
5. Neonatologist
Neonatologists are pediatricians with specialized training in the care of newborns, particularly those with medical complications or who are born prematurely. Their expertise is essential in managing complex medical conditions and ensuring the health and well-being of the newborn.
Care for Newborns with Complications:
- Premature Infants: Providing specialized care for premature infants in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs), addressing their unique medical needs and promoting growth and development.
- Medical Conditions: Managing newborns with congenital anomalies, respiratory distress, infections, and other medical conditions that require immediate intervention.
- Developmental Support: Offering guidance and support for families of newborns with ongoing medical needs, ensuring appropriate follow-up care and developmental assessments.
Collaboration with Other Healthcare Providers:
Neonatologists work closely with obstetricians, pediatricians, and other healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive care for newborns. This collaboration includes:
- Coordinated Care: Developing and implementing care plans tailored to the specific needs of each newborn, involving input from multiple specialists.
- Family Education: Providing education and support to families, helping them understand their newborn’s condition and the necessary steps for care and recovery.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Ensuring that newborns with ongoing medical needs receive appropriate follow-up care and monitoring to support healthy development.
Steps for Newborn Health Assessment:
Neonatologists conduct thorough assessments of newborns to identify any health issues and provide timely interventions:
- Apgar Score: Evaluate the newborn’s appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration (Apgar score) immediately after birth to assess overall health.
- Physical Examination: Perform a comprehensive physical examination to identify any congenital anomalies or medical conditions requiring attention.
- Diagnostic Testing: Order necessary laboratory tests and imaging studies to further evaluate the newborn’s health and guide treatment decisions.

6. Pediatrician
Pediatricians are medical doctors who specialize in the care of infants, children, and adolescents. They play a vital role in ensuring the health and development of newborns and providing ongoing care as the child grows.
Initial Care for Newborns:
- Newborn Examination: Conducting a thorough examination of the newborn shortly after birth to assess overall health and identify any immediate concerns.
- Monitoring Vital Signs: Continuously monitoring the newborn’s vital signs, including temperature, heart rate, and respiratory rate, to ensure stability and detect potential issues early.
- Vaccinations and Preventive Care: Administering the first doses of essential vaccines and providing guidance on preventive care to support the newborn’s health.
Monitoring Infant Health Post-Delivery:
Pediatricians provide ongoing care and monitoring to ensure healthy growth and development:
- Routine Check-Ups: Scheduling regular well-child visits to monitor growth, development, and overall health, addressing any concerns as they arise.
- Developmental Assessments: Conducting developmental screenings to identify potential delays or issues early, ensuring timely interventions and support.
- Parental Guidance: Offering education and support to parents on topics such as nutrition, sleep, and safety, empowering them to make informed decisions for their child’s health.
Guidelines for Newborn Health:
Pediatricians provide essential guidelines for parents to ensure the health and well-being of their newborns:
- Breastfeeding Support: Encouraging breastfeeding as the preferred method of nutrition for newborns, offering guidance and support to mothers to establish successful breastfeeding practices.
- Safe Sleep Practices: Educating parents on safe sleep practices to reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), including placing the baby on their back to sleep and using a firm mattress without loose bedding.
- Immunizations: Emphasizing the importance of timely immunizations to protect the newborn from infectious diseases and supporting parents in following the recommended vaccination schedule.
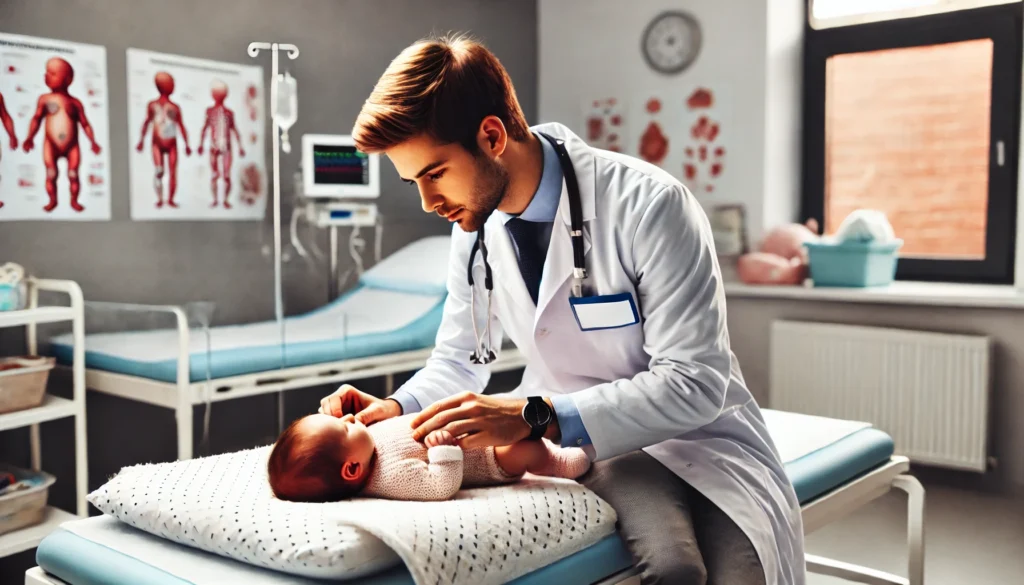

7. Doula
A doula is a trained professional who provides physical, emotional, and informational support to a mother before, during, and after childbirth. Unlike medical professionals, doulas do not perform clinical tasks but focus on providing continuous support to the mother and family.
Support for Emotional and Physical Needs:
- Prenatal Education: Offering education and resources to help the mother prepare for childbirth, including information on labor positions, pain management techniques, and what to expect during labor and delivery.
- Labor Support: Providing continuous support during labor, including physical comfort measures such as massage, positioning, and breathing techniques, as well as emotional reassurance and encouragement.
- Postpartum Support: Assisting the mother in the postpartum period with breastfeeding support, newborn care guidance, and emotional support as she adjusts to her new role.
Differences Between a Doula and a Midwife:
While both doulas and midwives support mothers during childbirth, their roles and responsibilities differ significantly:
- Clinical vs. Non-Clinical: Midwives are trained healthcare professionals who provide clinical care, while doulas focus on non-clinical support and advocacy.
- Medical Training: Midwives have medical training and are licensed to provide prenatal, labor, and postpartum care, whereas doulas do not perform medical procedures or make clinical decisions.
- Role in Birth Team: Doulas work alongside midwives, obstetricians, and other healthcare providers, complementing their care by focusing on the mother’s comfort and emotional well-being.
Importance of Continuous Support During Childbirth:
Research has shown that the presence of a doula during childbirth can have significant benefits:
- Reduced Interventions: Continuous support from a doula is associated with a lower likelihood of interventions such as epidurals, C-sections, and instrumental deliveries.
- Improved Birth Experience: Mothers who have the support of a doula often report higher satisfaction with their birth experience and a greater sense of empowerment.
- Enhanced Emotional Well-Being: Doulas provide reassurance and emotional support, helping to reduce anxiety and stress during childbirth and promoting a positive postpartum adjustment.
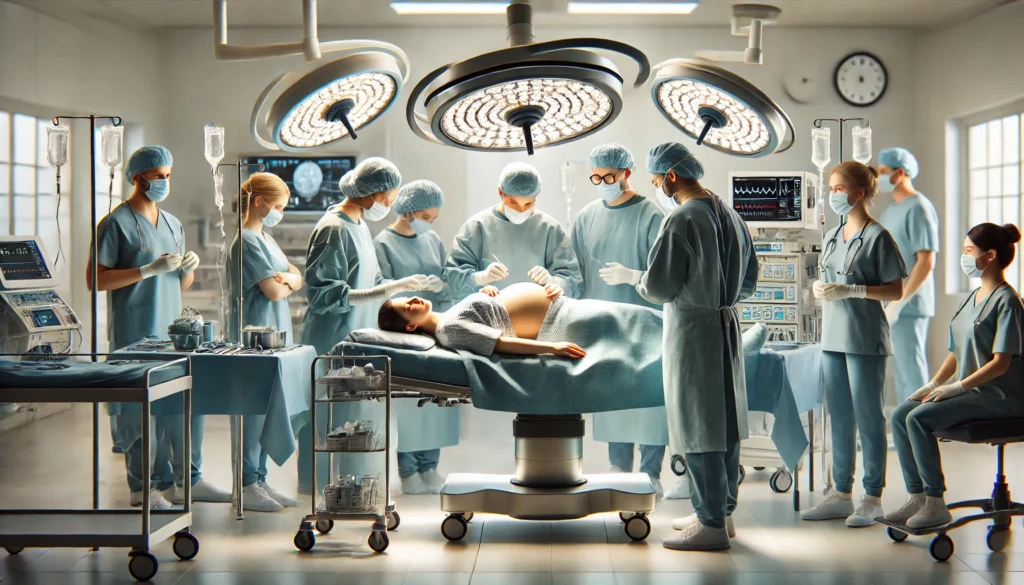
8. Lactation Consultant
Lactation consultants are healthcare professionals who specialize in supporting mothers with breastfeeding. They provide expert guidance and assistance to help mothers establish and maintain successful breastfeeding practices.
Assistance with Breastfeeding:
- Breastfeeding Education: Educating mothers about the benefits of breastfeeding, proper latch techniques, and positions to ensure effective breastfeeding.
- Addressing Challenges: Identifying and addressing common breastfeeding challenges such as latching difficulties, nipple pain, and low milk supply, offering practical solutions and support.
- Feeding Plans: Developing individualized feeding plans tailored to the mother’s and baby’s needs, ensuring adequate nutrition and growth for the newborn.
Education and Support for New Mothers:
Lactation consultants provide ongoing education and support to new mothers, helping them build confidence in their breastfeeding journey:
- In-Hospital Support: Offering in-hospital support immediately after delivery to help mothers initiate breastfeeding and address any concerns that arise in the early postpartum period.
- Home Visits: Conducting home visits to provide personalized support and guidance, addressing any breastfeeding challenges that may occur after leaving the hospital.
- Community Resources: Connecting mothers with community resources and support groups, fostering a sense of community and shared experience among breastfeeding mothers.
Tips for Successful Breastfeeding:
Lactation consultants offer practical tips to help mothers achieve successful breastfeeding:
- Early Initiation: Encourage early initiation of breastfeeding, ideally within the first hour after birth, to promote bonding and stimulate milk production.
- Frequent Feeding: Advise mothers to feed their newborns frequently, following the baby’s hunger cues and ensuring they receive adequate nutrition.
- Comfortable Positioning: Teach mothers how to position themselves and their baby comfortably to facilitate effective breastfeeding and reduce discomfort.

9. Perinatal Social Worker
Perinatal social workers are essential in providing comprehensive support to families during the perinatal period, helping them navigate the emotional, social, and practical challenges associated with childbirth and the transition to parenthood.
Resources and Referrals for Additional Help (continued):
- Mental Health Support: Connecting families with mental health resources, including therapists and support groups, to address issues such as postpartum depression and anxiety.
- Parenting Education: Offering educational resources on infant care, parenting techniques, and family dynamics to empower parents with knowledge and skills.
- Crisis Intervention: Providing crisis intervention services for families experiencing acute stressors, ensuring they receive timely and appropriate support.
Addressing Mental Health and Postpartum Depression:
Perinatal social workers play a critical role in identifying and addressing mental health concerns during the perinatal period:
- Screening and Assessment: Conducting screenings for postpartum depression and anxiety, identifying families at risk and facilitating early intervention.
- Supportive Counseling: Offering supportive counseling to mothers and families experiencing emotional distress, promoting resilience and coping strategies.
- Community Connections: Facilitating connections to community-based mental health services and support groups, ensuring families have access to ongoing support.

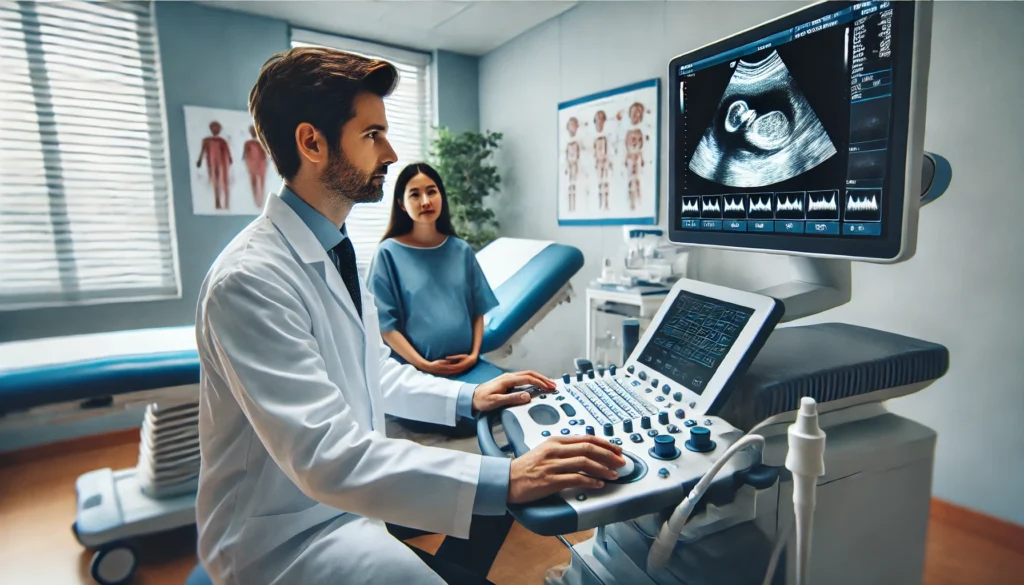
10. Sonographer
Sonographers are healthcare professionals who specialize in using ultrasound technology to create images of the fetus during pregnancy. They play a crucial role in prenatal care by providing valuable information about the baby’s development and identifying any potential concerns.
Role in Prenatal Care and Monitoring:
- Ultrasound Examinations: Performing routine ultrasound examinations to assess fetal growth, development, and position, as well as to detect any abnormalities.
- Diagnostic Imaging: Utilizing advanced imaging techniques to obtain detailed views of the fetus, placenta, and amniotic fluid, providing essential information for clinical decision-making.
- Collaboration with Healthcare Providers: Working closely with obstetricians and other healthcare providers to interpret ultrasound findings and ensure comprehensive prenatal care.
Use of Ultrasound Technology:
Ultrasound technology is a vital tool in prenatal care, offering numerous benefits:
- Non-Invasive: Ultrasound is a non-invasive and safe imaging technique that poses no risk to the mother or fetus, making it an ideal choice for prenatal monitoring.
- Real-Time Imaging: Provides real-time images of the fetus, allowing healthcare providers to observe movements, heartbeats, and other vital signs.
- Early Detection: Enables early detection of potential issues, such as congenital anomalies or growth restrictions, allowing for timely interventions and management.
Importance of Accurate Fetal Assessment:
Accurate fetal assessment is crucial for ensuring the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby:
- Growth Monitoring: Regular ultrasounds help track fetal growth and development, ensuring the baby is growing at a healthy rate and identifying any deviations from the norm.
- Anatomy Scans: Detailed anatomy scans assess the development of fetal organs and structures, identifying any abnormalities that may require further investigation or intervention.
- Positioning and Placenta: Ultrasound provides information on the baby’s position and the location of the placenta, which can impact delivery plans and decisions.
Conclusion
The process of childbirth is a complex and multifaceted event that requires the expertise and collaboration of a diverse team of healthcare professionals. From obstetricians and midwives to anesthesiologists and pediatricians, each professional plays a critical role in ensuring the health and safety of both the mother and the newborn.
This article has explored the roles and responsibilities of ten key healthcare professionals involved in the childbirth process, highlighting their contributions to a safe and successful delivery. By understanding the roles of these professionals and the importance of their collaboration, healthcare providers can better support mothers and families during this transformative time.
For doctors, adhering to best practices and guidelines is essential for providing high-quality care and promoting positive outcomes for mothers and newborns. For mothers, being informed and empowered about their childbirth options and the support available to them is crucial for making confident and informed decisions.
Ultimately, the successful delivery of a baby and the well-being of both the mother and newborn depend on a comprehensive and integrated approach to care, with each professional contributing their expertise and support. By fostering a collaborative and patient-centered approach, healthcare providers can ensure that every birth is a safe and positive experience, setting the foundation for a healthy and thriving future for both mother and child.
if you love sports car please visit this site
- 1970s American Cars
- Toyota MR2 Series
- 5 Used Sports Cars
- 2007 Lexus IS350 by Marty
- Alpine A110
- Love Letter to British Sports Cars
- Top 10 Best Affordable Sports Cars
- Audi TT to McLaren Senna
- 2023 Honda Civic SI
Guidelines for Newborn and Maternal Care
To ensure the health and well-being of both the newborn and the mother, it is important to follow established guidelines and best practices:
For Healthcare Providers:
- Provide Comprehensive Prenatal Care: Conduct regular prenatal visits to monitor the health of the mother and fetus, identify any risk factors, and provide education and support.
- Promote a Collaborative Approach: Foster collaboration among all members of the healthcare team to ensure coordinated and comprehensive care for the mother and newborn.
- Focus on Safety and Quality: Adhere to evidence-based practices and protocols to ensure a safe and high-quality childbirth experience, minimizing the risk of complications.
- Support Postpartum Recovery: Provide ongoing support and care for the mother in the postpartum period, addressing any physical or emotional challenges and promoting a smooth recovery.
For Mothers:
- Attend Regular Prenatal Visits: Regular prenatal visits are essential for monitoring your health and the health of your baby, ensuring early detection and management of any issues.
- Educate Yourself: Take advantage of educational resources and classes to learn about childbirth, breastfeeding, and newborn care, empowering yourself with knowledge and confidence.
- Follow a Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding harmful substances, to support the well-being of both you and your baby.
- Seek Support: Reach out for support from healthcare providers, family, and friends, and consider the benefits of having a doula or other support person during childbirth.
- Prioritize Mental Health: Pay attention to your emotional well-being and seek help if you experience feelings of anxiety, depression, or overwhelm during pregnancy or postpartum.
Ensuring a Healthy Life for Your Baby
The steps taken during pregnancy and childbirth have a lasting impact on the health and well-being of your baby. By following these guidelines, you can help ensure that your baby has a healthy start in life:
- Breastfeeding: Breastfeeding provides essential nutrients and antibodies that support your baby’s growth and immune system, offering numerous health benefits.
- Immunizations: Follow the recommended immunization schedule to protect your baby from preventable diseases and promote a healthy immune system.
- Safe Sleep Practices: Adhere to safe sleep guidelines to reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) and ensure a safe sleeping environment for your baby.
- Regular Check-Ups: Schedule regular pediatric check-ups to monitor your baby’s growth and development, address any concerns, and receive guidance on infant care.
- Nurturing Environment: Create a nurturing and supportive environment for your baby, fostering secure attachment and promoting healthy development.
In conclusion, the successful delivery of a baby and the health of both the mother and newborn rely on the expertise and collaboration of a dedicated team of healthcare professionals. By understanding their roles and responsibilities and following established guidelines for care, we can ensure a safe and positive childbirth experience and lay the foundation for a healthy and thriving future.
if you love stories then visit:


